In modernen Netzwerken hängen Effizienz und Zuverlässigkeit der Datenübertragung stark von den Vermittlungsmethoden ab, die von Netzwerkgeräten wie Switches und Routern eingesetzt werden. Drei Hauptmethoden dominieren diese Landschaft: Speichern und Weiterleiten, Cut-Throughund Adaptive Umschaltung. Jeder Modus bietet einzigartige Vorteile, die auf bestimmte Netzwerkumgebungen zugeschnitten sind. In diesem Artikel werden ihre Mechanismen, praktischen Anwendungen und SEO-optimierten Schlüsselwörter untersucht, damit Sie diese Technologien verstehen und effektiv einsetzen können.
1. Speicher- und Weiterleitungsschaltung
Wie es funktioniert
Store-and-Forward-Switching ist eine Methode, bei der der Switch den gesamten Datenrahmen empfängt und in einem Puffer speichert, bevor er ihn weiterleitet. Während dieses Prozesses führt der Switch kritische Prüfungen durch, wie z. B. Zyklische Redundanzprüfung (CRC), um Fehler zu erkennen. Nur fehlerfreie Rahmen werden übertragen, während beschädigte Rahmen verworfen werden711.
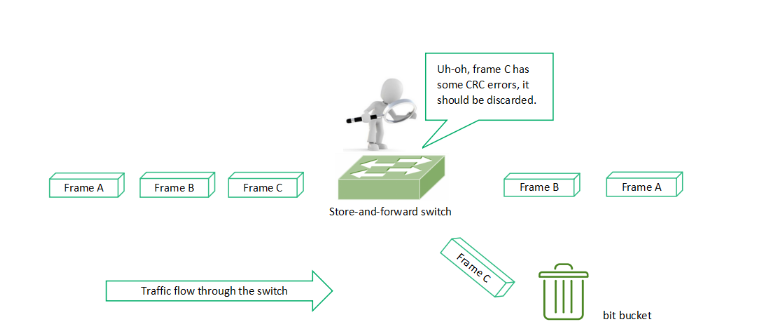
Wesentliche Merkmale
- Hohe Verlässlichkeit: Die Fehlererkennung gewährleistet die Datenintegrität und eignet sich daher ideal für unternehmenskritische Anwendungen wie Finanztransaktionen und Systeme im Gesundheitswesen715.
- Anpassung der Geschwindigkeit: Unterstützt die Kommunikation zwischen Geräten mit unterschiedlichen Geschwindigkeiten (z. B. 10 Mbit/s bis 100 Mbit/s), was die Kompatibilität in heterogenen Netzen verbessert713.
- Fortschrittliches Verkehrsmanagement: Ermöglicht komplexe Funktionen wie Quality of Service (QoS) und Access Control Lists (ACLs) durch Analyse des gesamten Rahmens1115.
Beeinträchtigungen
- Höhere Latenzzeit: Es kommt zu Verzögerungen bei der Verarbeitung aufgrund der Speicherung von Vollbildern und der Validierung111.
- Ressourcenintensiv: Benötigt viel Pufferspeicher, was in Umgebungen mit hohem Datenverkehr zu Überlastungen führen kann7.
Anwendungsfälle
- Unternehmensnetzwerke: Ideal für Umgebungen, in denen die Genauigkeit der Daten im Vordergrund steht, wie z. B. in Firmenbüros und Rechenzentren711.
- Gesundheitssysteme: Stellt sicher, dass Patientendaten (z. B. MRT-Scans) fehlerfrei übertragen werden7.
- Upgrades für ältere Netzwerke: Verbindet ältere und neuere Geräte mit unterschiedlichen Geschwindigkeitsanforderungen13.
2. Cut-Through Switching
Wie es funktioniert
Die Cut-Through-Vermittlung beginnt mit der Weiterleitung von Daten, sobald die Ziel-MAC-Adresse gelesen wird - in der Regel innerhalb der ersten 6 Bytes des Rahmens. Dies minimiert die Latenzzeit, überspringt aber die Fehlerprüfungen18.
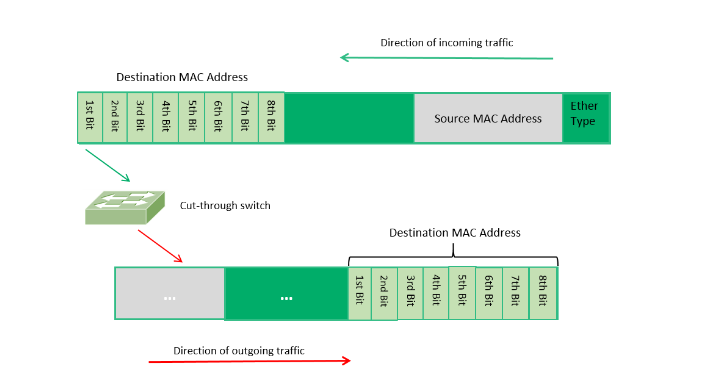
Wesentliche Merkmale
- Ultra-niedrige Latenzzeit: Die Verzögerungen bei der Weiterleitung werden reduziert auf 20 Mikrosekunden oder weniger, perfekt für Echtzeitanwendungen815.
- Hoher Durchsatz: Eliminiert Pufferungsverzögerungen und maximiert die Netzwerkleistung in Umgebungen mit geringen Fehlern111.
Beeinträchtigungen
- Keine Fehlererkennung: Beschädigte Rahmen (z. B. CRC-Fehler) verbreiten sich im Netz115.
- Eingeschränkte Funktionalität: Unterstützt keine Geschwindigkeitsumwandlung oder erweiterte Verkehrsrichtlinien13.
Anwendungsfälle
- Hochfrequenzhandel (HFT): An den Aktienmärkten, wo sich die Latenzzeit direkt auf die Gewinne auswirkt, kommt es auf Millisekunden an15.
- Videokonferenzen in Echtzeit: Sorgt für reibungslose Audio/Video-Synchronisation7.
- Fehlerarme Netzwerke: Glasfaser- oder gut gewartete Kupferinfrastrukturen, in denen Rahmenfehler selten sind811.
3. Adaptive Switching: Die Hybridlösung
Wie es funktioniert
Adaptive Switching schaltet dynamisch um zwischen Speichern und Weiterleiten und Cut-Through Modi auf der Grundlage der Echtzeit-Netzwerkbedingungen. So wird z. B. standardmäßig Cut-Through verwendet, um die Geschwindigkeit zu erhöhen, und auf Store-and-Forward umgeschaltet, wenn die Fehlerrate einen bestimmten Schwellenwert überschreitet813.
Wesentliche Merkmale
- Flexibilität: Gleichgewicht zwischen Geschwindigkeit und Zuverlässigkeit, Anpassung an die Verkehrsnachfrage8.
- Optimierte Leistung: Verringert die Latenzzeit im Normalbetrieb und gewährleistet gleichzeitig die Fehlerbehandlung bei Überlastung8.
Anwendungsfälle
- Hybride Netze: Kombiniert Echtzeitanwendungen (z. B. VoIP) mit Massendatenübertragungen (z. B. Backups)8.
- Dynamische Umgebungen: Campus-Netze mit schwankendem Verkehrsaufkommen13.
Vergleichende Analyse
| Umschaltmodus | Latenzzeit | Fehlerbehandlung | Am besten für |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speichern und Weiterleiten | Hoch | Ausgezeichnet | Finanzwesen, Gesundheitswesen, Altsysteme |
| Cut-Through | Ultra-niedrig | Keine | Handel in Echtzeit, Video-Streaming |
| Anpassungsfähig | Variabel | Mäßig | Umgebungen mit gemischtem Verkehrsaufkommen |
Schlussfolgerung
Die Wahl des richtigen Schaltmodus hängt von der Abwägung ab Geschwindigkeit, Zuverlässigkeitund Netzbedingungen. Während Store-and-Forward nach wie vor der Goldstandard für Genauigkeit ist, zeichnet sich Cut-Through in geschwindigkeitskritischen Szenarien aus. Adaptive Switching bietet einen vielseitigen Mittelweg und ist damit eine zukunftssichere Wahl für sich entwickelnde Netzwerke. Wenn Sie diese Modi auf Ihre betrieblichen Anforderungen abstimmen und SEO-Schlüsselwörter wie Cut-Through Switching und Adaptive Netzwerklösungenkönnen Sie sowohl die Netzwerkleistung als auch die Online-Sichtbarkeit optimieren.
















 SFP/SFP+ (1G/2.5G/5G/10G)
SFP/SFP+ (1G/2.5G/5G/10G) SFP-T (1G/2.5G/10G)
SFP-T (1G/2.5G/10G) AOC-Kabel 10G/25G/40G/100G
AOC-Kabel 10G/25G/40G/100G DAC-Kabel 10G/25G/40G/100G
DAC-Kabel 10G/25G/40G/100G QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G
QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G Kupfer-Glasfaser-Medienkonverter
Kupfer-Glasfaser-Medienkonverter Glasfaser-Medienkonverter PCBA-Platine
Glasfaser-Medienkonverter PCBA-Platine OEO Fiber Medienkonverter
OEO Fiber Medienkonverter Seriell-Glasfaser-Medienkonverter
Seriell-Glasfaser-Medienkonverter Video zu Glasfaser Medienkonverter
Video zu Glasfaser Medienkonverter 1000M GPON/EPON ONU
1000M GPON/EPON ONU 10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON
10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON 2.5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU
2.5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU POE GPON/EPON ONU
POE GPON/EPON ONU Drahtloser GPON/EPON ONT
Drahtloser GPON/EPON ONT EPON OLT
EPON OLT GPON OLT
GPON OLT SFP-PON-Modul
SFP-PON-Modul Industrielle Schalter
Industrielle Schalter Managed Switches
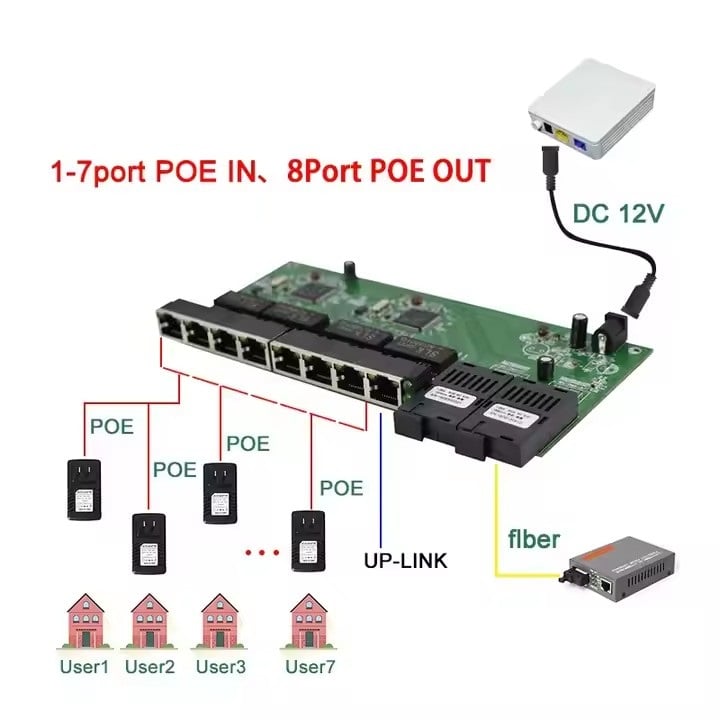
Managed Switches POE-Schalter
POE-Schalter Unmanaged Switches
Unmanaged Switches MTP/MPO-Glasfaserkabel
MTP/MPO-Glasfaserkabel Faseroptische Kassetten
Faseroptische Kassetten Fiber Optic Loopback
Fiber Optic Loopback Lichtwellenleiterkabel und Faserpigtails
Lichtwellenleiterkabel und Faserpigtails Optische Splitter und Splitterbox
Optische Splitter und Splitterbox Faserflansch-Verbinder
Faserflansch-Verbinder Optische Adapter
Optische Adapter Optisches Dämpfungsglied
Optisches Dämpfungsglied Schnellanschluss und Anschlussfeld
Schnellanschluss und Anschlussfeld CATV-Verstärker
CATV-Verstärker Optischer CATV-Empfänger
Optischer CATV-Empfänger Visuelle Fehlersuche
Visuelle Fehlersuche OTDR
OTDR Optischer Leistungsmesser
Optischer Leistungsmesser Faseroptische Kennung
Faseroptische Kennung Faseroptische Reiniger
Faseroptische Reiniger Fiber Cleavers & Fiber Strippers
Fiber Cleavers & Fiber Strippers Werkzeuge aus Kupfer
Werkzeuge aus Kupfer