- Émetteur-récepteur A+B :
Principe :
- Les émetteurs-récepteurs A+B utilisent deux fibres optiques distinctes, l'une pour la transmission des données en amont (canal A) et l'autre pour la transmission des données en aval (canal B).
- Les transmissions de données en amont et en aval sont complètement séparées et n'interfèrent pas entre elles. Avantages :
- La transmission séparée des données en amont et en aval garantit une grande efficacité de transmission et une forte capacité anti-interférence.
- Conception et mise en œuvre relativement simples.
- Sélection flexible des vitesses en amont et en aval en fonction des besoins réels. Inconvénients :
- Nécessite deux fibres optiques, ce qui entraîne une faible utilisation des ressources en fibres.
- Coûts d'installation et de câblage plus élevés.
- Monofibre BIDI(BIDI) :
Principe :
- Les émetteurs-récepteurs bidirectionnels à fibre unique (BIDI) utilisent une seule fibre optique, les données en amont et en aval étant transmises à l'aide de longueurs d'onde différentes.
- La technologie du multiplexage par répartition en longueur d'onde est utilisée pour réaliser une transmission de données bidirectionnelle sur une seule fibre. Avantages :
- Nécessite une seule fibre optique, ce qui permet une utilisation élevée des ressources en fibres.
- Coûts d'installation et de câblage moins élevés. Inconvénients :
- Les données en amont et en aval partagent une seule fibre, ce qui entraîne des interférences potentielles.
- Les vitesses en amont et en aval sont relativement limitées, en fonction des caractéristiques de la longueur d'onde optique.
- Une conception et une mise en œuvre plus complexes, entraînant des coûts plus élevés.
Dans le contexte des réseaux Gigabit, la technologie des émetteurs-récepteurs bidirectionnels à fibre unique (BIDI) est particulièrement avantageuse. Sa stabilité et sa rentabilité en font une solution idéale pour les déploiements à grande échelle dans les réseaux FTTH (Fiber-to-the-Home) et les réseaux de campus d'entreprise. Bien qu'il puisse y avoir des interférences entre les données en amont et en aval, le rapport coût-bénéfice global est plus élevé que celui des émetteurs-récepteurs A+B, qui conviennent mieux aux applications spécialisées ayant des exigences strictes en matière de performance et de fiabilité.












 SFP/SFP+ (1G/2,5G/5G/10G)
SFP/SFP+ (1G/2,5G/5G/10G) SFP-T (1G/2,5G/10G)
SFP-T (1G/2,5G/10G) Câble AOC 10G/25G/40G/100G
Câble AOC 10G/25G/40G/100G Câble DAC 10G/25G/40G/100G
Câble DAC 10G/25G/40G/100G QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G
QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G Convertisseurs de média cuivre-fibre
Convertisseurs de média cuivre-fibre Carte PCBA pour convertisseur de média à fibre optique
Carte PCBA pour convertisseur de média à fibre optique Convertisseurs de média à fibre optique OEO
Convertisseurs de média à fibre optique OEO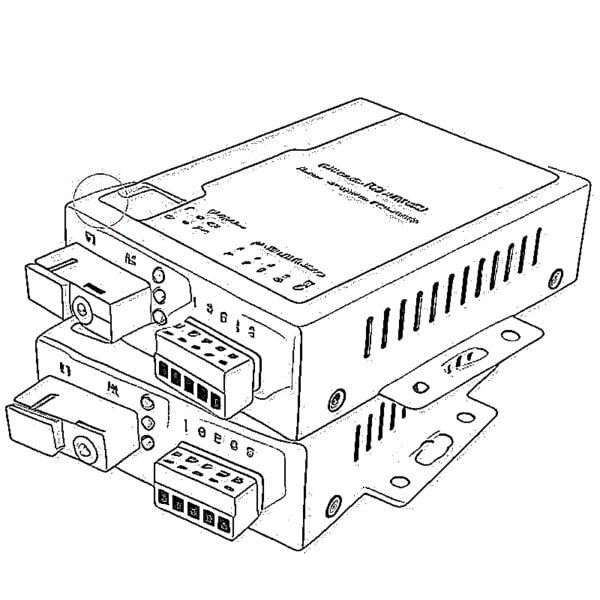 Convertisseurs de média série-fibre
Convertisseurs de média série-fibre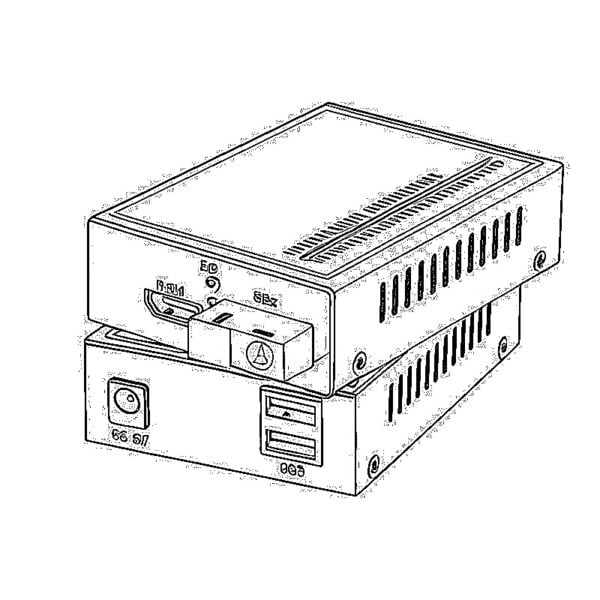 Convertisseurs vidéo vers fibre optique
Convertisseurs vidéo vers fibre optique 1000M GPON/EPON ONU
1000M GPON/EPON ONU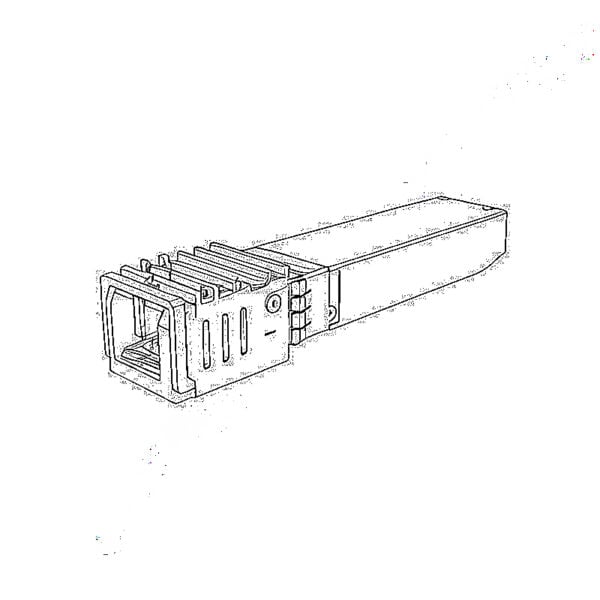 10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON
10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON 2,5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU
2,5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU POE GPON/EPON ONU
POE GPON/EPON ONU ONT GPON/EPON sans fil
ONT GPON/EPON sans fil EPON OLT
EPON OLT GPON OLT
GPON OLT Module PON SFP
Module PON SFP Interrupteurs industriels
Interrupteurs industriels Commutateurs administrables
Commutateurs administrables Commutateurs POE
Commutateurs POE Commutateurs non administrables
Commutateurs non administrables Câbles à fibres MTP/MPO
Câbles à fibres MTP/MPO Cassettes à fibres optiques
Cassettes à fibres optiques Boucle de fibre optique
Boucle de fibre optique Câbles optiques et pigtails de fibres
Câbles optiques et pigtails de fibres Répartiteurs optiques et boîtiers répartiteurs
Répartiteurs optiques et boîtiers répartiteurs Connecteurs à bride pour fibres
Connecteurs à bride pour fibres Adaptateurs optiques
Adaptateurs optiques Atténuateur optique
Atténuateur optique Connecteur rapide et panneau de connexion
Connecteur rapide et panneau de connexion Amplificateur CATV
Amplificateur CATV Récepteur optique CATV
Récepteur optique CATV Localisateur visuel de défauts
Localisateur visuel de défauts OTDR
OTDR Mesureur de puissance optique
Mesureur de puissance optique Identificateur de fibre optique
Identificateur de fibre optique Nettoyeurs de fibres optiques
Nettoyeurs de fibres optiques Coupe-fibres et dénudeurs de fibres
Coupe-fibres et dénudeurs de fibres Outils en cuivre
Outils en cuivre