Ядро оптического порта переключательИнтерфейс заключается в оптических модулях, а порты на панели коммутатора (например, слоты SFP/SFP+/QSFP28) предназначены для размещения этих модулей. Таким образом, стандарт интерфейса определяется типом используемого оптического модуля и средой передачи (тип оптоволокна).
Ниже приведены распространенные стандарты и типы интерфейсов, расположенные в порядке возрастания скорости передачи данных:
1. Гигабитный Ethernet (1G / 1000M)
Это наиболее распространенный тип базового оптического порта.
- Тип интерфейса/слота: SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable), широко известный как "маленький порт" или "гигабитный оптический порт".
- Общие стандарты оптических модулей:
- 1000BASE-SX: Используется многомодовое оптоволокно (MMF), типичное расстояние передачи 550 метров (при использовании оптоволокна OM2).
- 1000BASE-LX: Совместимость с многомодовым (передача на 550 метров) и одномодовым (SMF, передача до 10 км) оптоволокном.
- 1000BASE-ZX: Используется одномодовое оптоволокно, расстояние передачи 70-80 км.
- Используемый тип оптоволокна: Многомодовое оптоволокно (OM1/OM2/OM3/OM4) или одномодовое оптоволокно (OS2).
- Интерфейсный разъем: Обычно дуплекс LC; в некоторых старых устройствах используется дуплекс SC.
2. 10-гигабитный Ethernet (10G)
В настоящее время это основной тариф для ядра центров обработки данных и корпоративных сетей.
- Тип интерфейса/слота: SFP+ (Enhanced Small Form-factor Pluggable). Слоты SFP+ обратно совместимы с оптическими модулями SFP (но скорость передачи данных снижается до 1 Гбит/с).
- Общие стандарты оптических модулей:
- 10GBASE-SR: Используется многомодовое оптоволокно (OM3/OM4), расстояние передачи данных составляет 300 метров (OM3) и 400 метров (OM4) соответственно.
- 10GBASE-LR: используется одномодовое оптоволокно, расстояние передачи до 10 км.
- 10GBASE-ER: используется одномодовое оптоволокно, расстояние передачи до 40 км.
- 10GBASE-ZR: Используется одномодовое оптоволокно, расстояние передачи до 80 км.
- 10GBASE-T: Это стандарт электрических портов (с использованием сетевых кабелей), но некоторые коммутаторы также предлагают модули 10G-T в формате SFP+ для подключения по медному кабелю на короткие расстояния.
- Используемый тип оптоволокна: Многомодовое оптоволокно (OM3/OM4/OM5) или одномодовое оптоволокно.
- Интерфейсный разъем: LC дуплекс.
3. 25-гигабитный Ethernet (25G) и 40-гигабитный Ethernet (40G)
В основном они используются для высокоскоростного доступа к серверам и соединения коммутаторов.
- Тип интерфейса/слота:
- 25G: SFP28. Имеет тот же форм-фактор, что и SFP/SFP+, но поддерживает скорость передачи данных 25 Гбит/с.
- 40 Гбит/с: QSFP+ (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable). Один интерфейс QSFP+ объединяет 4 канала 10 Гбит/с.
- Общие стандарты оптических модулей:
- 25GBASE-SR: Используется многомодовое оптоволокно, расстояние передачи составляет около 70 метров (OM3) / 100 метров (OM4).
- 25GBASE-LR: используется одномодовое оптоволокно, расстояние передачи до 10 км.
- 40GBASE-SR4: Используется многомодовое оптоволокно с интерфейсом MPO/MTP, обеспечивающее передачу данных по 4-жильному параллельному каналу, с максимальным расстоянием 150 метров (OM4).
- 40GBASE-LR4: используется одномодовое волокно с интерфейсом LC, передающее 4 длины волны по одному волокну с помощью технологии WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing), с расстоянием передачи до 10 км.
- Используемый тип оптоволокна: Многомодовое оптоволокно (OM3/OM4/OM5) или одномодовое оптоволокно.
- Интерфейсный разъем: LC дуплекс (для стандартов LR) или MPO/MTP (12- или 24-жильный, для параллельной передачи SR4).
4. 100-гигабитный Ethernet (100G) и более высокие скорости
Они используются в ядрах центров обработки данных, магистральных сетях и высокоскоростных межсетевых соединениях.
- Тип интерфейса/слота:
- 100 ГБИТ/С: QSFP28. Он имеет тот же форм-фактор, что и QSFP+, но поддерживает 25 Гбит/с на канал, всего 4 канала (100 Гбит/с).
- 200 ГБИТ/С: QSFP56.
- 400 Гбит/с: QSFP-DD (Double Density) или OSFP (Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable). В настоящее время QSFP-DD является основным направлением.
- Общие стандарты оптических модулей (на примере 100 Гбит/с):
- 100GBASE-SR4: Используется многомодовое оптоволокно с интерфейсом MPO/MTP, обеспечивающее передачу 4x25G параллельно, с расстоянием передачи около 70 метров (OM4) / 100 метров (OM5).
- 100GBASE-LR4: используется одномодовое волокно с интерфейсом LC, передающее 4 длины волны (25 Гбит/с на длину волны) по одному волокну с помощью технологии WDM, расстояние передачи до 10 км.
- 100GBASE-ER4: аналогичен LR4, но расстояние передачи данных достигает 40 км.
- 100GBASE-DR: Используется одномодовое оптоволокно и интерфейс LC, с одноканальной модуляцией PAM4 на 100 Гбит/с, обеспечивающей передачу данных на расстояние до 500 метров. Это новое недорогое решение для передачи данных на короткие расстояния.
- Используемый тип оптоволокна: Многомодовое волокно (OM4/OM5) или одномодовое волокно. Одномодовое волокно широко используется для скоростей 400 Гбит/с и выше.
- Интерфейсный разъем: MPO/MTP (для параллельной передачи SR) или дуплексный LC (для передачи LR/WDM). В эпоху 400 Гбит/с появились новые разъемы, такие как CS и SN.
Сводная таблица
| Скорость передачи данных | Тип интерфейса/слота | Примеры общих стандартов оптических модулей | Типичное расстояние передачи | Распространенные волоконно-оптические устройства и разъемы |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Гбит/с | SFP | 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX, 1000BASE-ZX | 550 м, 10 км, 70 км | MMF/SMF, LC |
| 10 Гбит/с | СФП+ | 10GBASE-SR, 10GBASE-LR, 10GBASE-ER | 400 м, 10 км, 40 км | MMF/SMF, LC |
| 25 Гбит/с | SFP28 | 25GBASE-SR, 25GBASE-LR | 100 м, 10 км | MMF/SMF, LC |
| 40 Гбит/с | QSFP+ | 40GBASE-SR4, 40GBASE-LR4 | 150 м, 10 км | ММФ (МПО), СМФ (ЛК) |
| 100 Гбит/с | QSFP28 | 100GBASE-SR4, 100GBASE-LR4, 100GBASE-DR | 100 м, 10 км, 500 м | ММФ (МПО), СМФ (ЛК) |
| 400 Гбит/с | QSFP-DD / OSFP | 400GBASE-DR4, 400GBASE-FR4 | 500 м, 2 км | SMF (CS/SN/LC) |
Соображения по выбору
- Совместимость: Убедитесь, что оптический модуль совместим с маркой коммутатора. Хотя большинство коммутаторов поддерживают совместимые оптические модули сторонних производителей, некоторые марки (например, Cisco) могут блокировать оригинальные модули с помощью шифрования.
- Согласование типов волоконной оптики: Одномодовое оптоволокно (SMF/OS2) используется для передачи данных на большие расстояния; многомодовое оптоволокно (MMF/OM3/OM4/OM5) подходит для коротких расстояний и недорогих сценариев. Их нельзя смешивать, иначе возможен сбой связи или повреждение устройства.
- Расстояние передачи: Выбранный стандарт оптического модуля должен соответствовать фактическим требованиям к расстоянию передачи, с некоторым запасом.
- Длина волны: В разных стандартах используются различные длины волн (например, 850 нм, 1310 нм, 1550 нм), которые должны соответствовать типу оптоволокна и расстоянию передачи.
- Технология двунаправленной передачи: Например, двунаправленные (BiDi) оптические модули используют одно волокно для приема/передачи сигнала на разных длинах волн, что позволяет экономить ресурсы волокна.
Надеемся, что этот подробный обзор поможет вам полностью разобраться в стандартах интерфейсов и скоростях оптических портовых коммутаторов.
Оптические модульные трансиверы
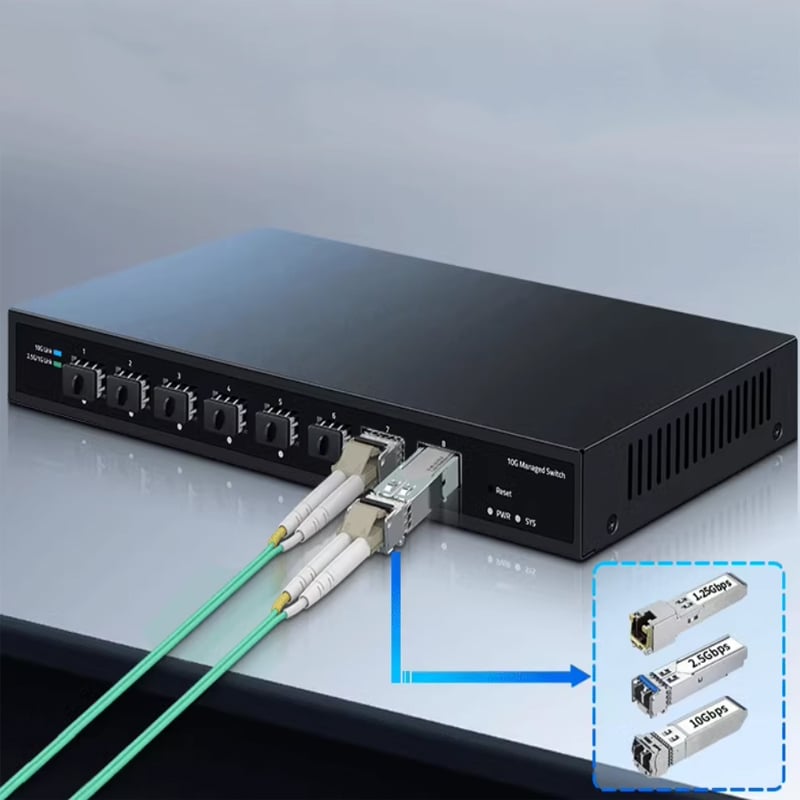












 SFP/SFP+ (1G/2.5G/5G/10G)
SFP/SFP+ (1G/2.5G/5G/10G) SFP-T (1G/2.5G/10G)
SFP-T (1G/2.5G/10G) Кабель AOC 10G/25G/40G/100G
Кабель AOC 10G/25G/40G/100G Кабель ЦАП 10G/25G/40G/100G
Кабель ЦАП 10G/25G/40G/100G QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G
QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G Медиаконвертеры из меди в оптоволокно
Медиаконвертеры из меди в оптоволокно Плата PCBA для оптоволоконного медиаконвертера
Плата PCBA для оптоволоконного медиаконвертера Оптоволоконные медиаконвертеры OEO
Оптоволоконные медиаконвертеры OEO Последовательные медиаконвертеры в оптоволоконные
Последовательные медиаконвертеры в оптоволоконные Видеоконвертеры в оптоволоконные медиаконвертеры
Видеоконвертеры в оптоволоконные медиаконвертеры 1000M GPON/EPON ONU
1000M GPON/EPON ONU 10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON
10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON 2,5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU
2,5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU POE GPON/EPON ONU
POE GPON/EPON ONU Беспроводной GPON/EPON ONT
Беспроводной GPON/EPON ONT ЭПОН ОЛТ
ЭПОН ОЛТ GPON-ОЛТ
GPON-ОЛТ Модуль SFP PON
Модуль SFP PON Промышленные коммутаторы
Промышленные коммутаторы Управляемые коммутаторы
Управляемые коммутаторы Коммутаторы POE
Коммутаторы POE Неуправляемые коммутаторы
Неуправляемые коммутаторы Волоконно-оптические кабели MTP/MPO
Волоконно-оптические кабели MTP/MPO Волоконно-оптические кассеты
Волоконно-оптические кассеты Волоконно-оптический шлейф
Волоконно-оптический шлейф Оптические кабели и волоконно-оптические пигтейлы
Оптические кабели и волоконно-оптические пигтейлы Оптические разветвители и разветвительные коробки
Оптические разветвители и разветвительные коробки Фланцевые соединители для оптоволокна
Фланцевые соединители для оптоволокна Оптические адаптеры
Оптические адаптеры Оптический аттенюатор
Оптический аттенюатор Быстроразъемное соединение и панель разъемов
Быстроразъемное соединение и панель разъемов Усилитель кабельного телевидения
Усилитель кабельного телевидения Оптический приемник кабельного телевидения
Оптический приемник кабельного телевидения Визуальный локатор неисправностей
Визуальный локатор неисправностей OTDR
OTDR Измеритель оптической мощности
Измеритель оптической мощности Волоконно-оптический идентификатор
Волоконно-оптический идентификатор Очистители оптоволокна
Очистители оптоволокна Скалыватели и стрипперные устройства для волокон
Скалыватели и стрипперные устройства для волокон Медные инструменты
Медные инструменты