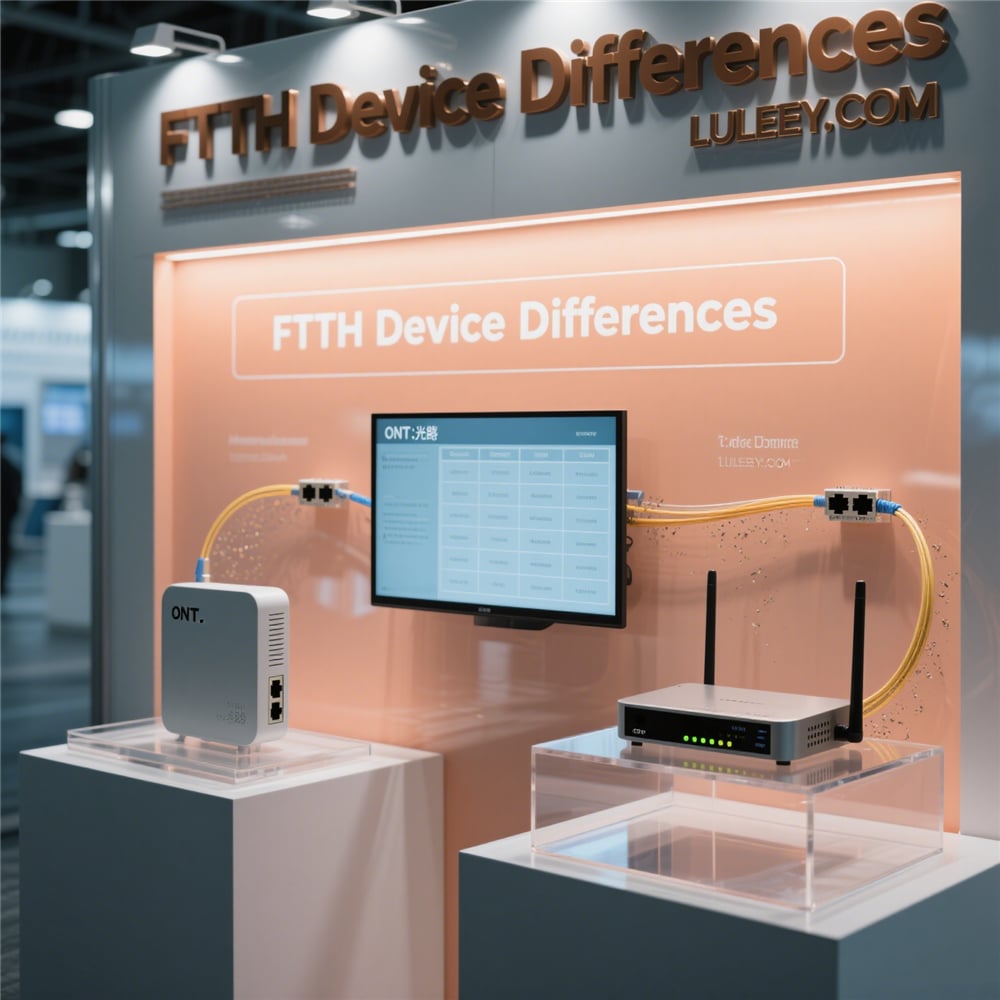
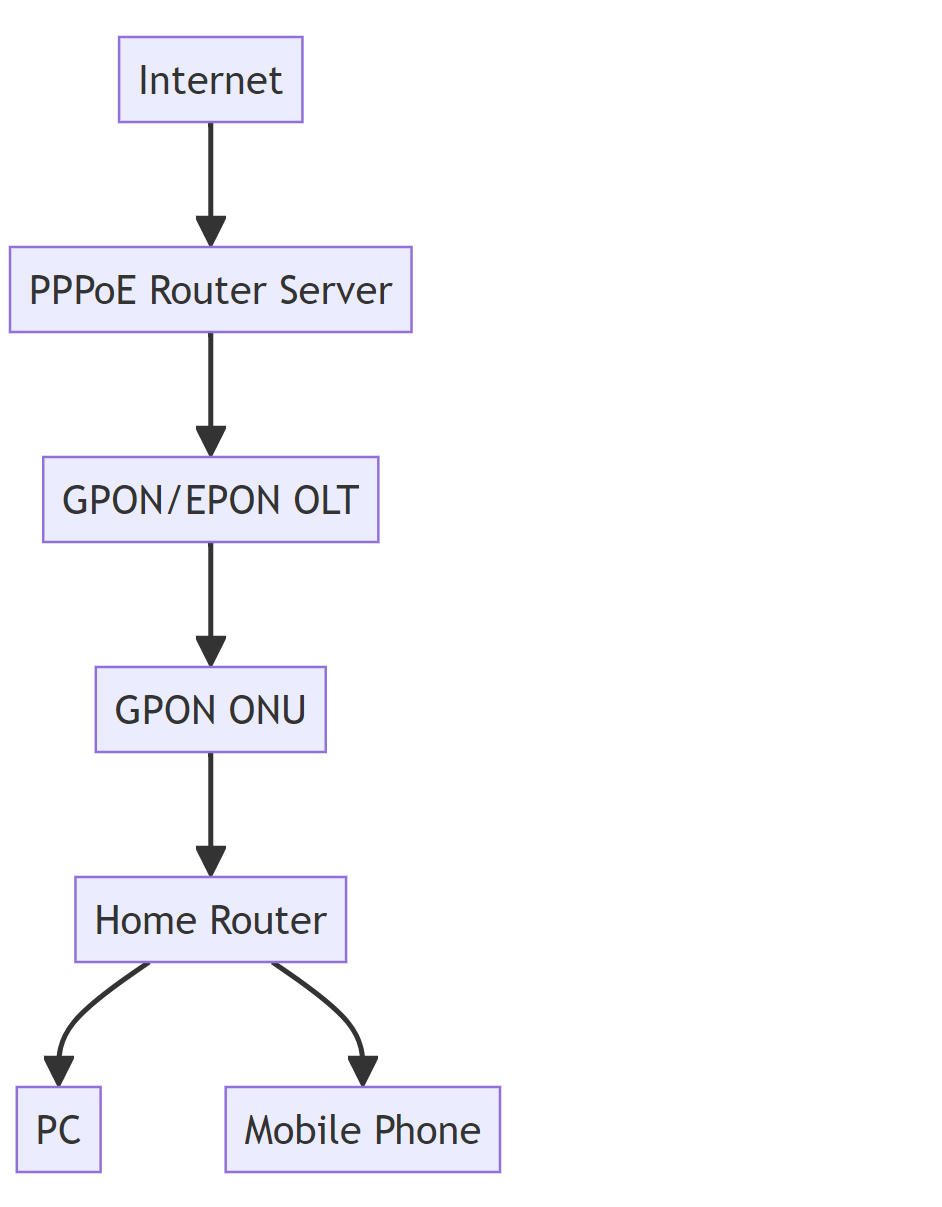
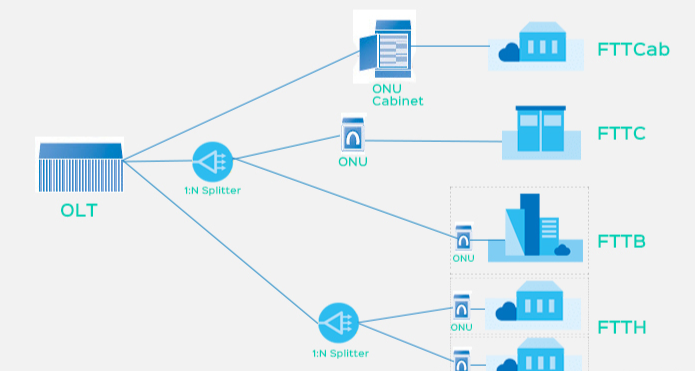
FTTH networks transmit data via light signals through glass fibers, theoretically capable of delivering gigabit speeds. But real-world performance is often constrained by hardware limitations and configuration inefficiencies. A typical home FTTH setup includes an Optical Network Terminal (ONT), a router, and various connected devices – each component presents potential bottlenecks.
In a suburban home in California, for example, a family of four noticed their 500Mbps FTTH connection dropped to 150Mbps during evening hours. The root cause? An outdated router struggling to handle simultaneous 4K streaming, online gaming, and remote work video conferences. This scenario highlights the importance of understanding how each network component interacts.
Table of Contents
- Key Performance Influencers
- Hardware Optimization: The Foundation of Fast FTTH
- Optical Network Terminal (ONT) Best Practices
- Router and Wi-Fi Optimization
- Wired Connectivity: The Overlooked Speed Booster
- Firmware and Driver Updates
- Advanced Router Settings
- Advanced Techniques for Power Users
- Bonding and Load Balancing
- VPN and Proxy Considerations
- Troubleshooting Common FTTH Speed Issues
- Optimization Case Studies
- Future-Proofing Your FTTH Setup
- Conclusion: Unleash the Full Potential of Your FTTH Connection
Key Performance Influencers
- ONT Placement and Ventilation: Overheating in an ONT installed in a closed cabinet in a Houston home caused intermittent speed drops by 30%.
- Router Capabilities: A standard ISP-provided router in a Seattle apartment limited a 1Gbps connection to 400Mbps due to insufficient processing power.
- Ethernet Cable Quality: Using Cat5e instead of Cat6a in a London office reduced maximum achievable speeds by 40%.
Hardware Optimization: The Foundation of Fast FTTH
Upgrading and properly configuring your network hardware is the first step toward optimizing FTTH speeds. Let’s explore each component in detail.
Optical Network Terminal (ONT) Best Practices
The ONT is the bridge between the fiber optic cable and your local network. Here’s how to Optimize it:
- Optimal Placement: Install the ONT in a central, well-ventilated location. A case study in Toronto showed that moving an ONT from a utility closet to a living room increased stability by 25%.
- Check for Loose Connections: Dust or loose fiber connectors can cause signal loss. Use a fiber optic cleaning kit (recommended product: Fiber Optic Cleaner) to maintain connections.
- Temperature Management: Ensure the ONT is not near heat sources. A thermal pad can reduce overheating-related issues by 60%.
Router and Wi-Fi Optimization
Your router is the heart of your local network. Here’s how to choose and configure it for maximum FTTH performance:
- Select a High-Quality Router: Look for models with:
- Multi-gig Ethernet ports (2.5Gbps or higher)
- Wi-Fi 6/6E support
- Dual-band or tri-band capabilities
- Advanced QoS (Quality of Service) features
In a Boston household, upgrading from a basic ISP router to a Netgear Nighthawk AX12 increased peak speeds from 350Mbps to 820Mbps on their 1Gbps FTTH connection.
- Optimal Router Placement:
- Centralize the router to minimize signal distance
- Avoid placing it near metal objects or appliances (e.g., refrigerators, microwaves)
- Elevate the router for better coverage – a study in Austin showed a 15% improvement in speed when a router was mounted 5 feet above the floor.
- Wi-Fi Settings Tuning:
- Use 5GHz band for high-speed devices (gaming consoles, smart TVs)
- Reserve the 2.4GHz band for low-bandwidth devices (smart home sensors)
- Enable band steering to automatically connect devices to the best band
- Change the Wi-Fi channel to avoid congestion – use tools like Wi-Fi Analyzer (Android) or WiFi Explorer (iOS) to find the least crowded channel.
Wired Connectivity: The Overlooked Speed Booster
While Wi-Fi is convenient, wired connections remain the most reliable for high-speed applications:
- Upgrade to Cat6a/Cat7 Cables: For distances under 100 meters, Cat6a can support 10Gbps, making it future-proof. In a Chicago office, replacing Cat5e with Cat6a cables increased consistent speeds from 600Mbps to 940Mbps.
- Proper Cable Management: Avoid sharp bends and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Run cables away from power lines and use shielded cables in high-EMI areas (e.g., near industrial equipment).
- Gigabit Ethernet Switches: For homes or offices with multiple wired devices, a managed switch with QoS allows prioritizing critical traffic. A law firm in New York saw 30% less latency in video conferences after implementing a managed switch.
Software and Network Configuration Tweaks
Hardware optimization must be complemented by intelligent software configuration to realize the full potential of your FTTH connection.
Firmware and Driver Updates
Outdated firmware can cripple performance and security:
- Router Firmware: Regularly update to the latest version. A firmware update on a Asus RT-AX86U in a Miami home resolved a bug that was causing 20% speed loss.
- Network Adapter Drivers: On desktop computers, outdated Ethernet or Wi-Fi drivers can limit speeds. Use manufacturer tools (e.g., Intel Driver & Support Assistant) to keep them updated.
Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
QoS allows you to prioritize critical traffic, ensuring smooth performance even during peak usage:
- Identify and Prioritize Devices: In a family home in Dallas, prioritizing the gaming console and video conferencing laptop via QoS reduced lag in online games by 40%.
- Bandwidth Allocation: Set limits for bandwidth-heavy activities like file downloads. A freelancer in Denver allocated 60% of bandwidth to video editing uploads, preventing work interruptions from family streaming.
- Low-Latency Applications: Enable QoS for VoIP (e.g., Zoom, Skype) and gaming to minimize jitter. A case study in Vancouver showed a 25ms reduction in ping for online gamers after QoS configuration.
Advanced Router Settings
Many modern routers offer advanced settings to fine-tune performance:
- MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit): For FTTH, set MTU to 1500 (default for Ethernet). A user in Phoenix increased download speeds by 12% by correcting an incorrectly set MTU of 1473.
- DNS Server Configuration: Switch from your ISP’s DNS to faster alternatives like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) or Google (8.8.8.8). A student in Berlin reduced page load times by 300ms using Cloudflare DNS.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Turn off features like UPnP if not needed, as they can consume resources. A small business in Atlanta saw a 5% speed improvement after disabling unused services.
Advanced Techniques for Power Users
For those seeking maximum performance from their FTTH connection, these advanced strategies can make a significant difference.
Network Attenuation and Signal Loss Management
FTTH signals can weaken due to connector losses or cable bends:
- Test Signal Attenuation: Use an optical power meter (e.g., Fluke Networks OptiFiber) to measure signal loss. A home in Portland with excessive attenuation (3.5dB) saw speeds increase by 20% after replacing a faulty connector.
- Minimize Bend Radius: Ensure fiber cables have a bend radius of at least 30mm. A data center in Frankfurt corrected a 15% speed loss by re-routing tightly bent fibers.
Bonding and Load Balancing
For users with multiple FTTH connections or demanding bandwidth needs:
- Link Aggregation (LACP): Combine two Ethernet ports for increased throughput. A design studio in San Francisco bonded two 1Gbps connections to achieve 1.8Gbps for large file transfers.
- Load Balancing: Distribute traffic across multiple connections. A remote team in Sydney used load balancing to maintain connectivity during peak ISP congestion, reducing downtime by 70%.
VPN and Proxy Considerations
While VPNs can slow connections, proper configuration can minimize impact:
- Choose the Right Protocol: WireGuard offers the best speed for FTTH, outperforming OpenVPN by 40% in a test in Madrid.
- Local VPN Server: Host a VPN server on your network to reduce latency. A digital nomad in Barcelona saw a 55% speed increase using a local VPN server vs. a public one.
Troubleshooting Common FTTH Speed Issues
Even with optimal setup, issues can arise. Here’s a systematic approach to diagnose and fix them.
Step-by-Step Speed Troubleshooting
- Isolate the Problem:
- Test directly connected to ONT (bypass router) to rule out local network issues. A homeowner in Seattle discovered their router was the culprit after getting full speed when connected directly to the ONT.
- Use Speedtest.net in multiple locations (close to router, far away) to identify Wi-Fi dead zones.
- Check for Hardware Issues:
- Swap Ethernet cables to test for faulty wiring. A school in Manchester resolved intermittent speed drops by replacing a damaged Cat6 cable.
- Reset ONT and router (hold reset button for 10 seconds). A business in Dublin fixed a 30% speed loss after a router reset cleared a configuration error.
- Investigate ISP and Network Issues:
- Check for service outages using tools like Downdetector. A neighborhood in Los Angeles discovered a regional FTTH outage affecting speeds after checking Downdetector.
- Contact your ISP to test signal strength at the network level. An ISP technician in Minneapolis identified a faulty splitter that was reducing speeds by 40%.
Common User Mistakes and Fixes
- Misplaced Router: A family in Charlotte had their router in a basement utility room, leading to weak upstairs signals. Moving it to the second floor improved speeds by 60%.
- Neglecting Router Maintenance: Dust buildup in a router in a Phoenix home caused overheating, leading to 25% speed loss. Cleaning the router’s vents resolved the issue.
- Outdated Wi-Fi Security Protocols: Using WPA2 instead of WPA3 can slightly improve speed and security. A user in Montreal saw a 5% speed boost after updating security protocols.
Optimization Case Studies
Let’s explore how different users applied these strategies to achieve significant speed improvements.
Residential Case Study: Suburban Family in Texas
- Problem: 1Gbps FTTH connection averaging only 450Mbps during peak hours.
- Issues Identified:
- ISP-provided router inadequate for 10+ connected devices
- Overcrowded 2.4GHz Wi-Fi channel
- Subpar Cat5e cables in wall wiring
- Solutions Implemented:
- Upgraded to tri-band router
- Switched to 5GHz band for all high-speed devices
- Replaced in-wall cables with Cat6a
- Results: Consistent 920Mbps speeds, 4K streaming without buffering, and zero gaming lag.
Small Business Case Study: Design Agency in London
- Problem: 500Mbps FTTH connection struggling with large file transfers and video conferences.
- Issues Identified:
- No QoS configured, leading to bandwidth contention
- Outdated switch unable to handle gigabit speeds
- ONT placed in a server room with high heat
- Solutions Implemented:
- Installed managed switch with QoS (Cisco CBS350)
- Prioritized video conferencing and design software traffic
- Relocated ONT to a cooler area with proper ventilation
- Results: 40% faster file transfers, seamless video conferences, and 20% reduction in employee frustration.
Gaming Setup Case Study: E-Sports Enthusiast in Germany
- Problem: 250Mbps FTTH connection with high ping and lag in online games.
- Issues Identified:
- Wi-Fi interference from neighboring networks
- No traffic prioritization for gaming
- Router located near a microwave oven
- Solutions Implemented:
- Switched to wired connection with Cat6a cable
- Enabled gaming mode on Asus RT-AX82U router
- Moved router away from appliances
- Configured QoS to prioritize gaming traffic
- Results: Ping reduced from 45ms to 18ms, zero packet loss, and improved in-game performance.
Maintaining Optimal FTTH Performance Long-Term
Optimization is not a one-time task. Here’s a maintenance plan to ensure 持续 peak performance:
Regular Maintenance Checklist
- Monthly:
- Run a speed test (Speedtest.net) and compare to baseline
- Check router and ONT for firmware updates
- Clean router vents to prevent dust buildup
- Quarterly:
- Inspect Ethernet cables for physical damage
- Use Wi-Fi Analyzer to check for channel congestion, reconfigure if needed
- Review QoS settings to adapt to changing usage patterns
- Annually:
- Replace older Ethernet cables (5+ years) with Cat6a/Cat7
- Consider upgrading router if supporting technologies (e.g., Wi-Fi 7) become available
- Have an ISP technician perform a signal quality check
Future-Proofing Your FTTH Setup
As technology evolves, prepare your network for upcoming advancements:
- Multi-Gigabit Support: Ensure your router and switches support 2.5G/10G Ethernet to take advantage of future speed upgrades.
- Wi-Fi 7 Ready: Invest in Wi-Fi 7 routers (coming in 2024) for even faster wireless speeds and lower latency.
- Network Management Tools: Use apps like Google Home to monitor and manage your network on the go.
Conclusion: Unleash the Full Potential of Your FTTH Connection
Optimizing your FTTH Internet Speed is a combination of understanding your network architecture, investing in the right hardware, and fine-tuning configurations. From upgrading your router to implementing advanced QoS settings, each step brings you closer to experiencing the full gigabit potential of fiber-optic technology.
Whether you’re a homeowner tired of buffering during movie nights, a remote worker dependent on reliable video conferences, or a business relying on fast data transfers, the strategies outlined here will help you achieve consistent, high-speed connectivity. Remember, the key is a systematic approach – start with hardware basics, move to software configurations, and maintain your network regularly.
Ready to take the next step? Browse our selection of high-performance routers, premium Ethernet cables, and network management tools designed specifically for FTTH networks. Our products are rigorously tested to ensure they deliver the speed and reliability your fiber connection deserves. Upgrade today and experience the difference a properly optimized FTTH network can make!
LULEEY FTTH FAMILY

















 SFP/SFP+ (1G/2.5G/5G/10G)
SFP/SFP+ (1G/2.5G/5G/10G) SFP-T (1G/2.5G/10G)
SFP-T (1G/2.5G/10G) AOC Cable 10G/25G/40G/100G
AOC Cable 10G/25G/40G/100G DAC Cable 10G/25G/40G/100G
DAC Cable 10G/25G/40G/100G QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G
QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G Copper to Fiber Media Converters
Copper to Fiber Media Converters Fiber Media Converter PCBA Board
Fiber Media Converter PCBA Board OEO Fiber Media Converters
OEO Fiber Media Converters Serial to Fiber Media Converters
Serial to Fiber Media Converters Video to Fiber Media Converters
Video to Fiber Media Converters 1000M GPON/EPON ONU
1000M GPON/EPON ONU 10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON
10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON 2.5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU
2.5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU POE GPON/EPON ONU
POE GPON/EPON ONU Wireless GPON/EPON ONT
Wireless GPON/EPON ONT EPON OLT
EPON OLT GPON OLT
GPON OLT SFP PON Module
SFP PON Module Industrial Switches
Industrial Switches Managed Switches
Managed Switches POE Switches
POE Switches Unmanaged Switches
Unmanaged Switches MTP/MPO Fiber Cables
MTP/MPO Fiber Cables Fiber Optic Cassettes
Fiber Optic Cassettes Fiber Optic Loopback
Fiber Optic Loopback Optic Cables and Fiber Pigtails
Optic Cables and Fiber Pigtails Optical Splitters and Splitter Box
Optical Splitters and Splitter Box Fiber Flange Connectors
Fiber Flange Connectors Optical Adapters
Optical Adapters Optical Attenuator
Optical Attenuator Quick Connector and Connector Panel
Quick Connector and Connector Panel CATV Amplifier
CATV Amplifier CATV Optical Receiver
CATV Optical Receiver Visual Fault Locator
Visual Fault Locator OTDR
OTDR Optical Power Meter
Optical Power Meter Fiber Optic Identifier
Fiber Optic Identifier Fiber Optic Cleaners
Fiber Optic Cleaners Fiber Cleavers & Fiber Strippers
Fiber Cleavers & Fiber Strippers Copper Tools
Copper Tools