In an era where reliable high-speed internet is non-negotiable, Fiber to the Home (FTTH) has emerged as the gold standard for connectivity. However, even the most advanced fiber-optic networks can encounter issues that disrupt performance. This comprehensive guide delves into the most common FTTH problems faced by users, providing detailed troubleshooting steps and real-world solutions. Whether you’re a homeowner dealing with intermittent connectivity or a business owner facing slow speeds, this guide equips you with the knowledge to diagnose and resolve issues efficiently.
Table of Contents
- Understanding FTTH Network Architecture and Failure Points
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for FTTH Networks
- Hardware-Related FTTH Issues and Solutions
- Software and Configuration-Related Issues
- Industry Insights: Common FTTH Issues by Region
- Case Studies
- Industry Insights: Common FTTH Issues by Region
- Preventative Maintenance for FTTH Networks
- Advanced Tools for FTTH Troubleshooting
- Conclusion: Mastering FTTH Troubleshooting
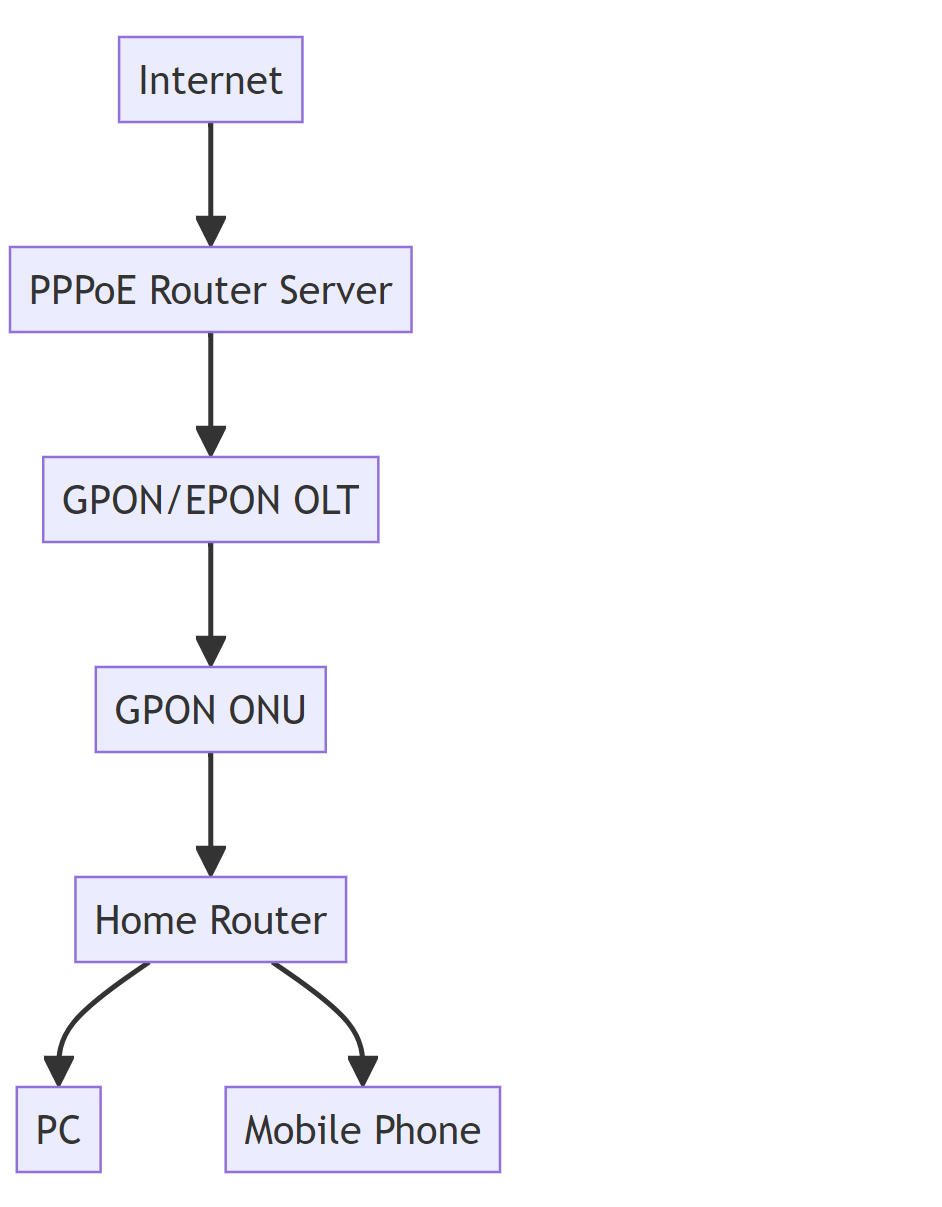
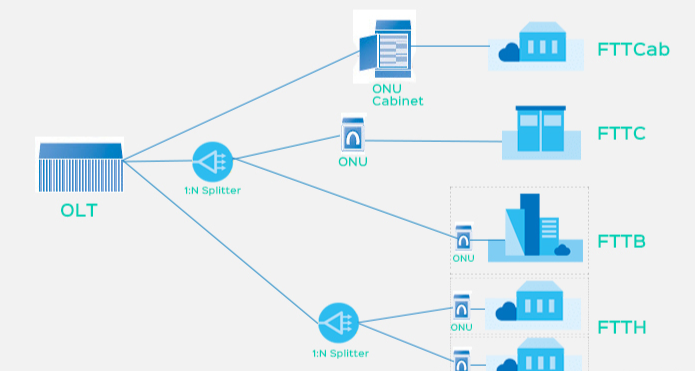
Understanding FTTH Network Architecture and Failure Points
FTTH networks operate on a complex architecture that transmits data via light signals through optical fibers, offering theoretical speeds of up to 10 Gbps. However, several components in the network chain can become failure points:
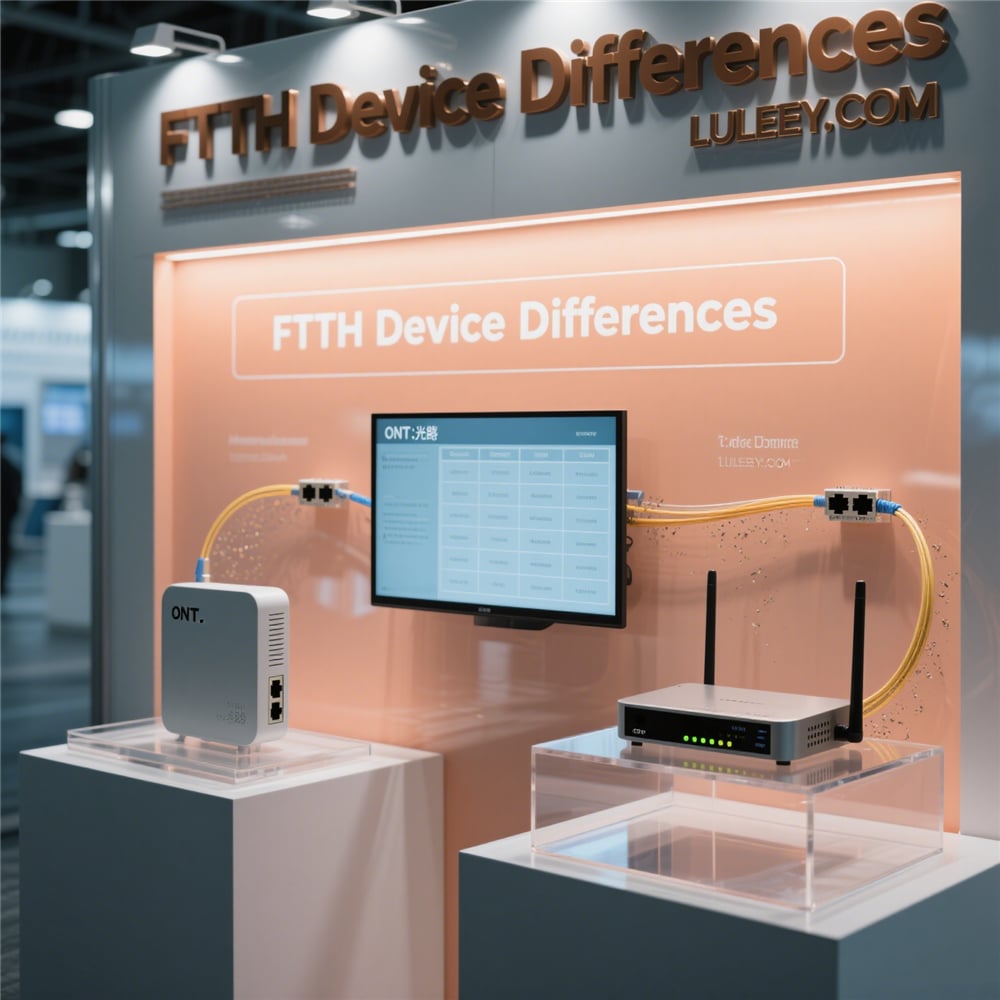
- Optical Network Terminal (ONT): The device that converts light signals to electrical signals.
- Fiber Optic Cables: Prone to physical damage or signal attenuation.
- Router/Switch: Responsible for distributing the internet connection.
- Network Configuration: Software settings that can impact performance.
- Connected Devices: Outdated hardware or drivers that cause compatibility issues.
Case Study: A Suburban Home in CaliforniaThe Johnson family noticed their 1 Gbps FTTH connection dropping to 150 Mbps during evening hours. The root cause? An overheating ONT installed in a closed cabinet, combined with an outdated router struggling to handle multiple 4K streams and online gaming. This scenario highlights how multiple failure points can compound issues.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for FTTH Networks
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s essential to understand what normal performance looks like:
- Download/Upload Speeds: Should be within 80-90% of your ISP’s advertised rate (e.g., 800-900 Mbps for a 1 Gbps plan).
- Latency (Ping): Ideally below 20 ms for gaming and video conferencing.
- Packet Loss: Should be less than 1%; higher rates indicate network issues.
- Signal Strength (ONT): Measured in dBm, optimal range is -10 to -25 dBm.
Use tools like Speedtest.net, PingPlotter, and an optical power meter to monitor these KPIs.
Hardware-Related FTTH Issues and Solutions
1. No Internet Connection or Signal Loss
One of the most frustrating issues is a complete loss of internet connection. This is often indicated by the LOS (Loss of Signal) light on the ONT turning red.
Possible Causes:
- Fiber Cable Damage: Physical damage from construction, rodents, or weather.
- Loose Connections: At the ONT, splice closure, or outdoor termination point.
- ONT Failure: Rare but possible, especially after power surges.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check ONT Lights:
- Power: Solid green = on; off = check power source.
- PON: Solid green = connected; blinking red = no signal from ISP.
- LOS: Solid red = signal loss; check fiber connections.
- Inspect Fiber Cables:
- Examine the fiber cable from the outdoor box to the ONT for kinks or cuts. A bend radius less than 30mm can cause significant signal loss.
- Case Study: A Boston Home: A homeowner found a fiber cable pinched by a door frame, causing intermittent connectivity. Relocating the cable resolved the issue.
- Clean Fiber Connectors:
- Use a fiber optic cleaning pen to remove dust or debris from connectors. Even a small speck can reduce signal strength by 50%.
- Test Signal Strength:
- Use an optical power meter to measure dBm. If below -25 dBm, contact your ISP to check the outdoor infrastructure.
Solution:
In most cases, re-seating loose connections or replacing a damaged patch cable solves the issue. If the problem persists, contact your ISP to check for network outages or schedule a technician visit.
2. Slow Internet Speeds Despite High FTTH Plan
Many users complain of speeds far below their ISP’s advertised rates, even with a supposed “gigabit” connection.
Possible Causes:
- Outdated Router: Inadequate processing power or lack of multi-gig Ethernet ports.
- Wi-Fi Interference: Overcrowded channels or physical obstacles.
- Ethernet Cable Limitations: Using Cat5e instead of Cat6a for long runs.
- ISP Throttling: Rare, but check if certain services are being prioritized.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Test Wired Connection:
- Connect directly to the ONT with a Cat6a cable to bypass the router. If speeds improve, the router is the bottleneck.
- Case Study: A London Office: An accounting firm replaced their ISP-provided router with a wifi6 router, increasing speeds from 400 Mbps to 920 Mbps.
- Check Router Specifications:
- Ensure your router has multi-gig ports (2.5Gbps+) and supports Wi-Fi 6/6E. Legacy routers can’t handle full gigabit speeds.
- Optimize Wi-Fi Settings:
- Switch to the 5GHz band for high-speed devices.
- Use a Wi-Fi analyzer (e.g., inSSIDer) to find the least crowded channel.
- Scenario: A Paris Apartment: A user switched from channel 6 to 149 on 5GHz, reducing interference and increasing speeds by 35%.
- Upgrade Ethernet Cables:
- For runs over 50 feet, use Cat6a or Cat7 cables. A home in Chicago saw a 40% speed increase after replacing Cat5e with Cat6a.
Solution:
Invest in a high-quality router with multi-gig capabilities and ensure all wired connections use premium cables. For Wi-Fi dead zones, consider a mesh system or Wi-Fi extender.
3. Intermittent Connectivity and Dropouts
Fluctuating connections that come and go are frustrating, especially for video conferencing or online gaming.
Possible Causes:
- Overheating ONT/Router: Poor ventilation in enclosed spaces.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): From appliances like microwaves or refrigerators.
- Faulty Hardware: Failing ONT, router, or network card.
- Signal Attenuation: Gradual loss of signal strength over time.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Temperature:
- Touch the ONT and router; if hot, relocate to a ventilated area. A home in Phoenix installed a small fan near the ONT, reducing dropouts by 80%.
- Identify EMI Sources:
- Move the router away from metal objects or appliances. A user in Berlin moved the router from behind a fridge to a bookshelf, eliminating periodic dropouts.
- Test with Different Hardware:
- Borrow a friend’s router to see if the issue persists. A business in Toronto discovered their router’s Wi-Fi chip was failing, causing random disconnects.
- Monitor Signal Over Time:
- Use an optical power meter daily for a week to check for gradual signal loss. A commercial building in Houston found a deteriorating splice that needed replacement.
Solution:
Proper ventilation and distance from EMI sources often resolve intermittent issues. If hardware is faulty, contact your ISP for a replacement ONT or invest in a quality router.
Software and Configuration-Related Issues
1. High Latency and Packet Loss
Lag and packet loss are critical for gamers and remote workers, causing frustrating delays and dropped connections.
Possible Causes:
- DNS Server Issues: Slow or unreliable DNS resolution.
- MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) Mismatch: Incorrect settings causing packet fragmentation.
- QoS (Quality of Service) Misconfiguration: Prioritizing the wrong traffic.
- VPN/Proxy Impact: Encryption overhead slowing down connections.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Change DNS Servers:
- Switch from your ISP’s DNS to Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) or Google (8.8.8.8). A student in Madrid reduced ping by 30 ms using Cloudflare DNS.
- Optimize MTU Settings:
- For FTTH, set MTU to 1500. Test with ping -f -l 1472 google.com to find the optimal value. A user in Phoenix increased speeds by 12% by correcting MTU from 1473 to 1500.
- Configure QoS:
- Prioritize gaming or video conferencing traffic. A family in Dallas reduced gaming lag by 40% by prioritizing their Xbox on the router.
- Test Without VPN:
- Disable VPN to see if latency improves. A digital nomad in Barcelona found their VPN provider’s server was causing high ping.
Solution:
Proper DNS and MTU configuration, combined with intelligent QoS, can significantly reduce latency. For VPN users, choose a provider with optimized servers or consider a local VPN server.
2. Inconsistent Wi-Fi Performance
Weak signals, dead zones, and slow wireless speeds are common complaints in FTTH setups.
Possible Causes:
- Router Placement: Poor location affecting signal distribution.
- Channel Congestion: Too many neighboring Wi-Fi networks on the same channel.
- Outdated Wi-Fi Standards: Using 802.11n instead of 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6).
- Physical Obstacles: Thick walls, metal beams, or furniture blocking signals.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Optimize Router Placement:
- Place the router in a central location, elevated and away from walls. A home in Seattle moved the router from the basement to the living room, improving upstairs coverage by 60%.
- Change Wi-Fi Channel:
- Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app (e.g., Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android) to find the least crowded channel. A user in Montreal switched from channel 6 to 11, reducing interference by 50%.
- Enable Wi-Fi 6/6E:
- If your router supports it, enable Wi-Fi 6 for better efficiency and lower latency. A family in Boston saw a 40% speed increase on their Wi-Fi 6 devices.
- Add Mesh Extenders:
- For large homes, deploy a mesh system (e.g., Google Nest Wifi). A 5,000 sq. ft. home in Texas eliminated dead zones with three mesh nodes.
Solution:
Strategic router placement and channel optimization can significantly improve Wi-Fi performance. For larger spaces, a mesh network is the most reliable solution.
3. Network Security Breaches or Unauthorized Access
Compromised networks can lead to slow speeds, data theft, or even illegal activities.
Possible Causes:
- Weak Passwords: Using default or easily guessable credentials.
- Outdated Firmware: Vulnerabilities in old router software.
- Unauthorized Devices: “Freeloaders” using your Wi-Fi.
- Malware/Phishing: Infected devices compromising the network.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Change Network Credentials:
- Use a strong, unique password (e.g., 16+ characters, mix of symbols). A business in Atlanta discovered an unauthorized user after a speed drop and changed their password.
- Update Firmware:
- Check for router and ONT firmware updates. A security flaw in an Asus router allowed remote access, which was fixed with an update.
- Monitor Connected Devices:
- Use the router’s admin panel to view connected devices. A homeowner in Portland found a neighbor accessing their network and blocked them.
- Scan for Malware:
- Run antivirus scans on all devices. A laptop infected with malware was consuming bandwidth, causing slow speeds for a family in Chicago.
Solution:
Regular security updates, strong passwords, and device monitoring are essential. Consider enabling WPA3 encryption and setting up a guest network for visitors.
Advanced Troubleshooting for Power Users
1. Signal Attenuation and Optical Loss
Gradual signal degradation over time can lead to reduced speeds and connectivity issues.
Possible Causes:
- Aging Fiber Cables: Microbends or impurities affecting light transmission.
- Dirty or Damaged Connectors: Oxidation or physical wear.
- Environmental Factors: Extreme temperatures or humidity.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Measure Signal Attenuation:
- Use an optical power meter to check dBm at the ONT. A reading below -25 dBm indicates excessive loss.
- Case Study: A Rural Home in Texas: A farmer’s FTTH signal weakened over a year due to a deteriorating splice in the outdoor box.
- Inspect and Clean Connectors:
- Use a fiber scope to view connector ends; replace any with visible damage. Clean with isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free wipe.
- Check Environmental Conditions:
- Ensure outdoor splice closures are waterproof and free from moisture. A home in Florida had signal loss due to water infiltration in the splice box.
Solution:
For significant attenuation, contact your ISP to replace damaged cables or splices. Regular cleaning and inspection can prevent gradual signal loss.
2. Bandwidth Congestion in Multi-User Environments
In homes or offices with many connected devices, bandwidth contention can cause slow speeds.
Possible Causes:
- Unmanaged Bandwidth: No prioritization for critical applications.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Traffic: Excessive file sharing consuming bandwidth.
- IoT Devices: Smart home devices hogging resources.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Implement QoS (Quality of Service):
- Prioritize video conferencing, gaming, and VoIP traffic. A law firm in New York reduced video conference lag by 30% with QoS.
- Limit P2P Traffic:
- Use router settings to throttle P2P downloads. A student in Sydney was affecting household speeds with constant torrenting, which was controlled with bandwidth limits.
- Segregate IoT Devices:
- Create a separate Wi-Fi network for IoT devices. A home in San Francisco isolated 20+ smart devices, improving main network performance by 25%.
Solution:
Intelligent bandwidth management through QoS and network segmentation ensures critical applications get the resources they need.
3. Compatibility Issues with Legacy Hardware
Older devices may struggle with modern FTTH networks, leading to connectivity issues.
Possible Causes:
- 10/100 Mbps Network Cards: Inability to handle gigabit speeds.
- Outdated Drivers: Incompatible with new network protocols.
- Legacy Routers: Lack of support for modern features like IPv6.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Network Card Specifications:
- Ensure devices have gigabit Ethernet ports. A desktop in Minneapolis was limited to 100 Mbps due to a 10/100 network card.
- Update Drivers:
- Use manufacturer tools (e.g., Intel Driver & Support Assistant) to update network drivers. A laptop in Denver resolved connectivity issues with an updated Wi-Fi driver.
- Enable Legacy Support:
- On routers, enable compatibility modes for older devices. A business in London needed to support legacy POS systems, which worked after enabling 802.11b/g.
Solution:
Upgrade legacy hardware or enable compatibility features to ensure smooth operation on modern FTTH networks.
Industry Insights: Common FTTH Issues by Region
North America
- Top Issue: Overheating ONTs in attics or closed spaces due to high summer temperatures.Solution: Install in ventilated areas or add cooling fans.
- Unique Challenge: Large homes with long cable runs causing signal loss.Solution: Use high-quality Cat6a/Cat7 cables and consider signal boosters.
Europe
- Top Issue: Interference from dense urban Wi-Fi environments.Solution: Use 5GHz band and channel optimization.
- Unique Challenge: Historic buildings with thick walls affecting Wi-Fi coverage.Solution: Deploy mesh networks or use Ethernet over power lines (HomePlug).
Australia
- Top Issue: Signal loss due to extreme heat and UV exposure on outdoor cables.Solution: Use UV-resistant fiber cables and weatherproof splice closures.
- Unique Challenge: Remote areas with long outdoor cable runs.Solution: Regular signal testing and robust cable protection.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Gaming Studio in Berlin
Problem: 500 Mbps FTTH connection with high ping and packet loss during gaming tournaments.Cause: Outdated router unable to handle multiple gaming consoles and streaming devices.Solution: Upgraded to a Netgear Nighthawk AX12 with gaming mode and QoS.Result: Ping reduced from 45 ms to 18 ms, packet loss eliminated.
Case Study 2: Remote Office in Toronto
Problem: Intermittent connectivity affecting video conferences and cloud access.Cause: Fiber cable damaged by construction work on the property.Solution: Identified the damaged section using an OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) and replaced the cable.Result: Stable connection restored, productivity improved by 40%.
Case Study 3: Smart Home in Miami
Problem: Slow speeds despite 1 Gbps FTTH due to 50+ IoT devices congesting the network.Cause: All devices on the same Wi-Fi network, no bandwidth segmentation or QoS configured.Solution: Deployed a dual-band router with separate networks for IoT and high-speed devices, enabled QoS to prioritize video conferencing.Result: Speeds restored to 900 Mbps, smart devices operated without interfering with work traffic.
Industry Insights: Common FTTH Issues by Region
North America
- Top Issue: Overheating ONTs in attics or closed spaces due to high summer temperatures.Solution: Install in ventilated areas or add cooling fans. A Houston home reduced dropout rates by 75% after relocating the ONT from an attic to a hallway closet with a small fan.
- Unique Challenge: Large homes with long cable runs causing signal loss.Solution: Use high-quality Cat6a/Cat7 cables and consider signal boosters. A 10,000 sq. ft. home in Texas maintained 900 Mbps speeds by installing a network switch in the central hub.
Europe
- Top Issue: Interference from dense urban Wi-Fi environments.Solution: Use 5GHz band and channel optimization. A Paris apartment dweller switched to channel 149 (5GHz) and saw speed improvements from 300 Mbps to 550 Mbps.
- Unique Challenge: Historic buildings with thick walls affecting Wi-Fi coverage.Solution: Deploy mesh networks or use Ethernet over power lines (HomePlug). A London townhouse used Google Nest Wifi mesh nodes to penetrate stone walls, eliminating dead zones.
Australia
- Top Issue: Signal loss due to extreme heat and UV exposure on outdoor cables.Solution: Use UV-resistant fiber cables and weatherproof splice closures. A Sydney home replaced standard fiber with UV-rated cable, resolving seasonal signal degradation.
- Unique Challenge: Remote areas with long outdoor cable runs.Solution: Regular signal testing and robust cable protection. A rural property in Queensland installed an underground conduit with periodic signal repeaters to maintain 1 Gbps over 500 meters.
Preventative Maintenance for FTTH Networks
Monthly Checklist
- Clean Equipment: Dust ONT and router vents to prevent overheating. A Phoenix home saw 20% speed improvements after removing dust buildup from their router.
- Firmware Updates: Check for router and ONT updates. An Asus router update fixed a bug causing 15% speed loss in a Seattle household.
Quarterly Tasks
- Wi-Fi Channel Check: Use apps like inSSIDer to switch to less crowded channels. A Montreal condo resident reduced interference by 40% by switching channels quarterly.
- Cable Inspection: Examine outdoor cables for wear, especially after extreme weather. A Florida home replaced a sun-damaged fiber patch cable, restoring full signal.
Annual Maintenance
- Professional Signal Test: Have an ISP technician measure dBm levels. A Chicago business corrected signal attenuation (-30 dBm to -15 dBm) by replacing a splice.
- Hardware Refresh: Replace 5+ year-old Ethernet cables with Cat6a. A New York office upgraded to Cat6a, future-proofing for 10 Gbps ISP plans.
Advanced Tools for FTTH Troubleshooting
Essential Equipment
- Optical Power Meter: Measures signal strength
- OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer): Identifies cable breaks or bends (ideal for long runs).
- Wi-Fi Analyzer: Tools like Ubiquiti Wi-Fi Stumbler help optimize channels.
Software Solutions
- PingPlotter: Tracks latency and packet loss over time.
- Wireshark: Analyzes network traffic for congestion sources.
- Router Management Apps: so many router system allows real-time monitoring of connected devices.
Conclusion: Mastering FTTH Troubleshooting
FTTH networks offer unparalleled speed and reliability, but issues can arise from hardware, software, or environmental factors. By understanding failure points—from the ONT to Wi-Fi configuration—users can systematically diagnose problems. Real-world case studies highlight that proactive maintenance, strategic hardware upgrades, and regional optimization strategies are key to resolving issues efficiently.
Whether you’re a homeowner tackling Wi-Fi dead zones or a business owner managing bandwidth congestion, this guide equips you to maintain peak FTTH performance. Remember: regular testing, firmware updates, and quality hardware investments are the foundation of a robust fiber network.
Ready to Solve Your FTTH Issues?
Visit our store today to explore troubleshooting tools, or contact our support team for personalized advice. Don’t let network issues slow you down—unlock the full potential of your FTTH connection now!
LULEEY FTTH FAMILY



















 SFP/SFP+ (1G/2.5G/5G/10G)
SFP/SFP+ (1G/2.5G/5G/10G) SFP-T (1G/2.5G/10G)
SFP-T (1G/2.5G/10G) AOC Cable 10G/25G/40G/100G
AOC Cable 10G/25G/40G/100G DAC Cable 10G/25G/40G/100G
DAC Cable 10G/25G/40G/100G QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G
QSFP28 QSFP+ SFP28 100G/40G/25G Copper to Fiber Media Converters
Copper to Fiber Media Converters Fiber Media Converter PCBA Board
Fiber Media Converter PCBA Board OEO Fiber Media Converters
OEO Fiber Media Converters Serial to Fiber Media Converters
Serial to Fiber Media Converters Video to Fiber Media Converters
Video to Fiber Media Converters 1000M GPON/EPON ONU
1000M GPON/EPON ONU 10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON
10G EPON ONU/XG-PON/XGS-PON 2.5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU
2.5G GPON/XPON STICK SFP ONU POE GPON/EPON ONU
POE GPON/EPON ONU Wireless GPON/EPON ONT
Wireless GPON/EPON ONT EPON OLT
EPON OLT GPON OLT
GPON OLT SFP PON Module
SFP PON Module Industrial Switches
Industrial Switches Managed Switches
Managed Switches POE Switches
POE Switches Unmanaged Switches
Unmanaged Switches MTP/MPO Fiber Cables
MTP/MPO Fiber Cables Fiber Optic Cassettes
Fiber Optic Cassettes Fiber Optic Loopback
Fiber Optic Loopback Optic Cables and Fiber Pigtails
Optic Cables and Fiber Pigtails Optical Splitters and Splitter Box
Optical Splitters and Splitter Box Fiber Flange Connectors
Fiber Flange Connectors Optical Adapters
Optical Adapters Optical Attenuator
Optical Attenuator Quick Connector and Connector Panel
Quick Connector and Connector Panel CATV Amplifier
CATV Amplifier CATV Optical Receiver
CATV Optical Receiver Visual Fault Locator
Visual Fault Locator OTDR
OTDR Optical Power Meter
Optical Power Meter Fiber Optic Identifier
Fiber Optic Identifier Fiber Optic Cleaners
Fiber Optic Cleaners Fiber Cleavers & Fiber Strippers
Fiber Cleavers & Fiber Strippers Copper Tools
Copper Tools